An up-to-date list is available on Google Scholar.
2024
-
×
![]()
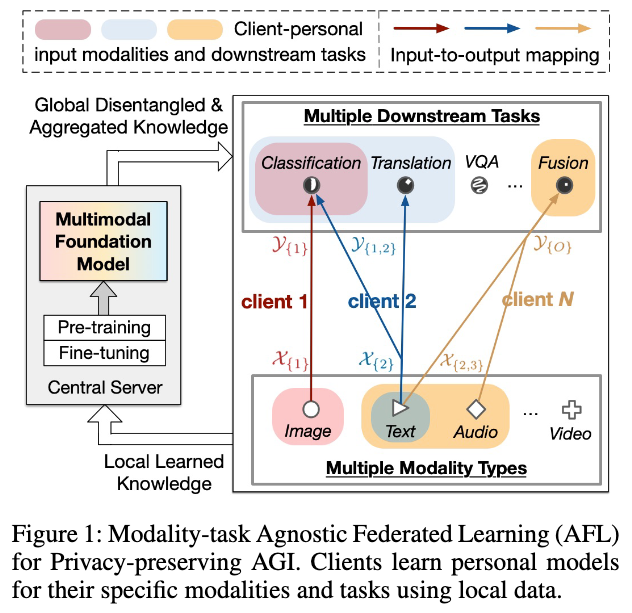
On Disentanglement of Asymmetrical Knowledge Transfer for Modality-Task Agnostic Federated Learning
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In AAAI (Oral), 2024
There has been growing concern regarding data privacy during the development and deployment of Multimodal Foundation Models for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), while Federated Learning (FL) allows multiple clients to collaboratively train models in a privacy-preserving manner. This paper formulates and studies Modality-task Agnostic Federated Learning (AFL) to pave the way toward privacy-preserving AGI. A unique property of AFL is the asymmetrical knowledge relationships among clients due to modality gaps, task gaps, and domain shifts between clients. This raises a challenge in learning an optimal inter-client information-sharing scheme that maximizes positive transfer and minimizes negative transfer for AFL. However, prior FL methods, mostly focusing on symmetrical knowledge transfer, tend to exhibit insufficient positive transfer and fail to fully avoid negative transfer during inter-client collaboration. To address this issue, we propose DisentAFL, which leverages a two-stage Knowledge Disentanglement and Gating mechanism to explicitly decompose the original asymmetrical inter-client information-sharing scheme into several independent symmetrical inter-client information-sharing schemes, each of which corresponds to certain semantic knowledge type learned from the local tasks.
2023
-
×
![]()
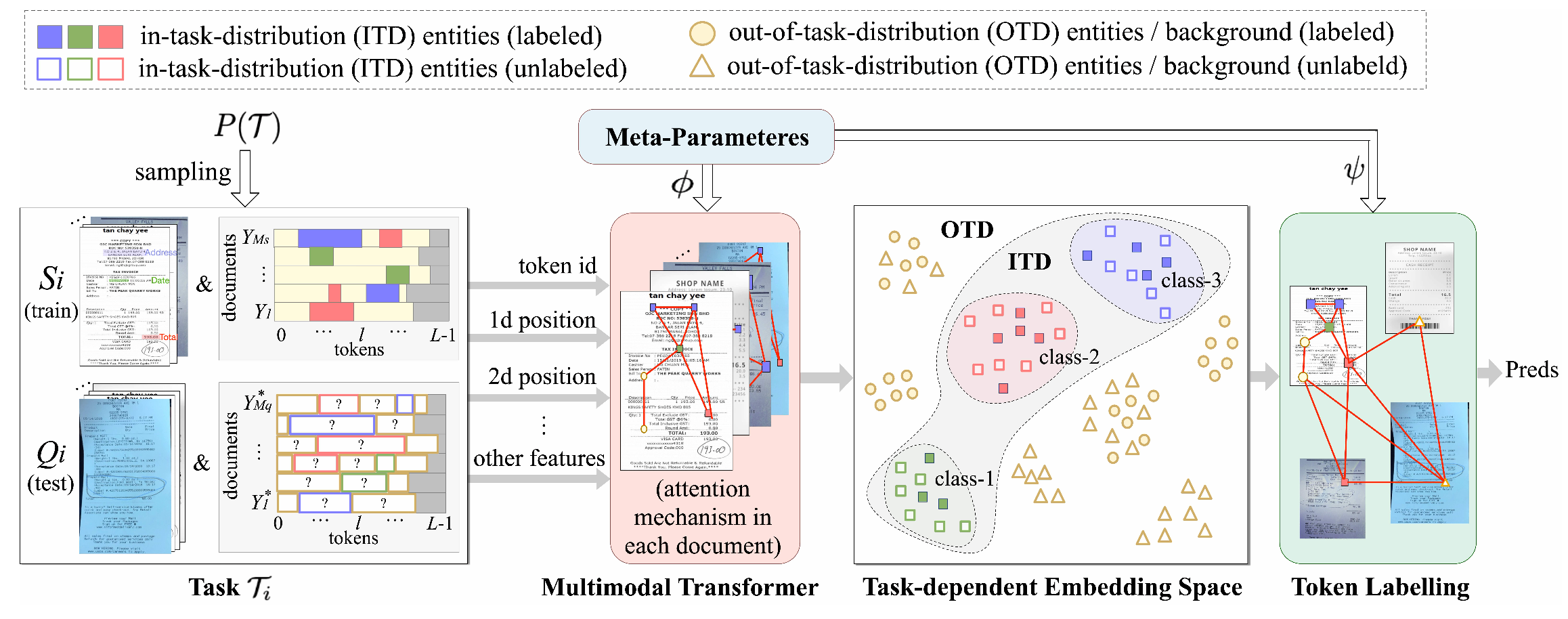
On Task-personalized Multimodal Few-shot Learning for Visually-rich Document Entity Retrieval
Jiayi Chen, Hanjun Dai, Bo Dai, Aidong Zhang, and Wei Wei
In EMNLP Findings, 2023
Visually-rich document entity retrieval (VDER), which extracts key information (e.g. date, address) from document images like invoices and receipts, has become an important topic in industrial NLP applications. The emergence of new document types at a constant pace, each with its unique entity types, presents a unique challenge: many documents contain unseen entity types that occur only a couple of times. Addressing this challenge requires models to have the ability of learning entities in a few-shot manner. However, prior works for Few-shot VDER mainly address the problem at the document level with a predefined global entity space, which doesn’t account for the entity-level few-shot scenario: target entity types are locally personalized by each task and entity occurrences vary significantly among documents. To address this unexplored scenario, this paper studies a novel entity-level few-shot VDER task. The challenges lie in the uniqueness of the label space for each task and the increased complexity of out-of-distribution (OOD) contents. To tackle this novel task, we present a task-aware meta-learning based framework, with a central focus on achieving effective task personalization that distinguishes between in-task and out-of-task distribution. Specifically, we adopt a hierarchical decoder (HC) and employ contrastive learning (ContrastProtoNet) to achieve this goal. Furthermore, we introduce a new dataset, FewVEX, to boost future research in the field of entity-level few-shot VDER. Experimental results demonstrate our approaches significantly improve the robustness of popular meta-learning baselines.
-
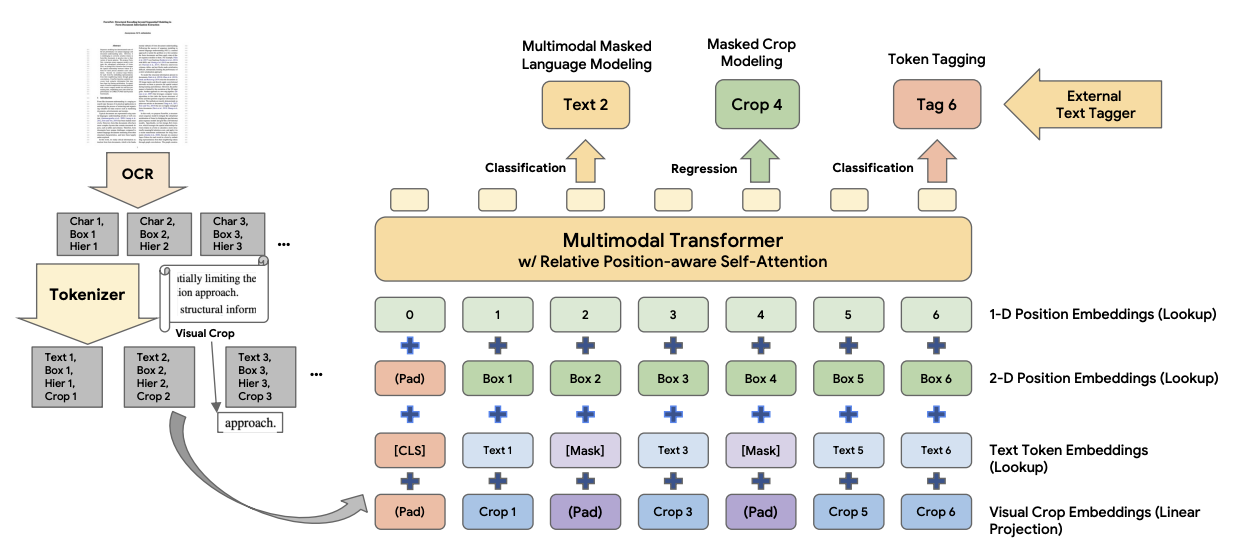
DocumentNet: Bridging the Data Gap in Document Pre-Training
Lijun Yu, Jin Miao, Xiaoyu Sun, Jiayi Chen, Alexander G. Hauptmann, Hanjun Dai, and Wei Wei
In EMNLP Industry Track, 2023
Document understanding tasks, in particular, Visually-rich Document Entity Retrieval (VDER), have gained significant attention in recent years thanks to their broad applications in enterprise AI. However, publicly available data have been scarce for these tasks due to strict privacy constraints and high annotation costs. To make things worse, the non-overlapping entity spaces from different datasets hinder the knowledge transfer between document types. In this paper, we propose a method to collect massive-scale and weakly labeled data from the web to benefit the training of VDER models. The collected dataset, named DocumentNet, does not depend on specific document types or entity sets, making it universally applicable to all VDER tasks. The current DocumentNet consists of 30M documents spanning nearly 400 document types organized in a four-level ontology. Experiments on a set of broadly adopted VDER tasks show significant improvements when DocumentNet is incorporated into the pre-training for both classic and few-shot learning settings. With the recent emergence of large language models (LLMs), DocumentNet provides a large data source to extend their multi-modal capabilities for VDER.
-
×
![]()
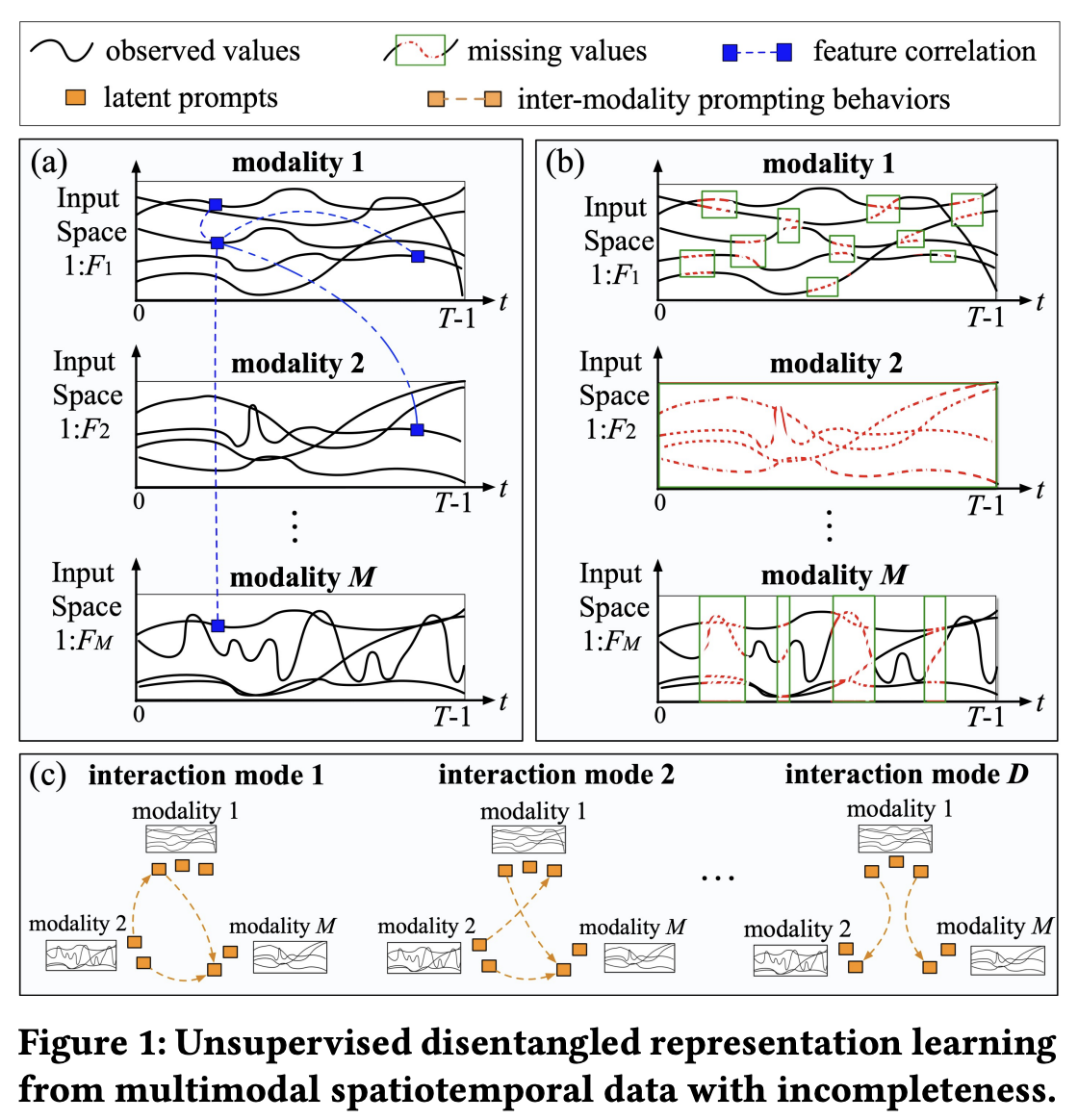
On Hierarchical Disentanglement of Interactive Behaviors for Multimodal Spatiotemporal Data with Incompleteness
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In Proceedings of the 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’23): Research Track, 2023
Multimodal spatiotemporal data (MST) consists of multiple simultaneous spatiotemporal modalities that interact with each other in a dynamic manner. Due to the complexity of MST and the recent desire for the explainability of artificial intelligent systems, disentangled representation learning for MST (DisentMST) has become a significant task, which aims to learn disentangled representations that can expose the underlying spatial semantics, temporal dynamic patterns, and inter-modality interaction modes of the complex MST. One limitation of existing approaches is that they might fail to tolerate the real-world incomplete MST data, where missing information might break the cross-modal spatiotemporal dynamics and bring noise and ambiguity to the learning process. Another limitation is that no existing work systematically reveals the structure of different types of disentangled information. To tackle the two limitations, we define a novel two-level hierarchically structured disentanglement task for MST, which reveals informative and structured disentangled representations for MST as well as digests the real-world MST with incompleteness. We propose a new framework, BiDisentMST, which leverages Gaussian Processes and Graph Factorization on the latent space to achieve our purposes. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework compared with baselines with respect to disentanglement and imputation results.
2022
-
×
![]()
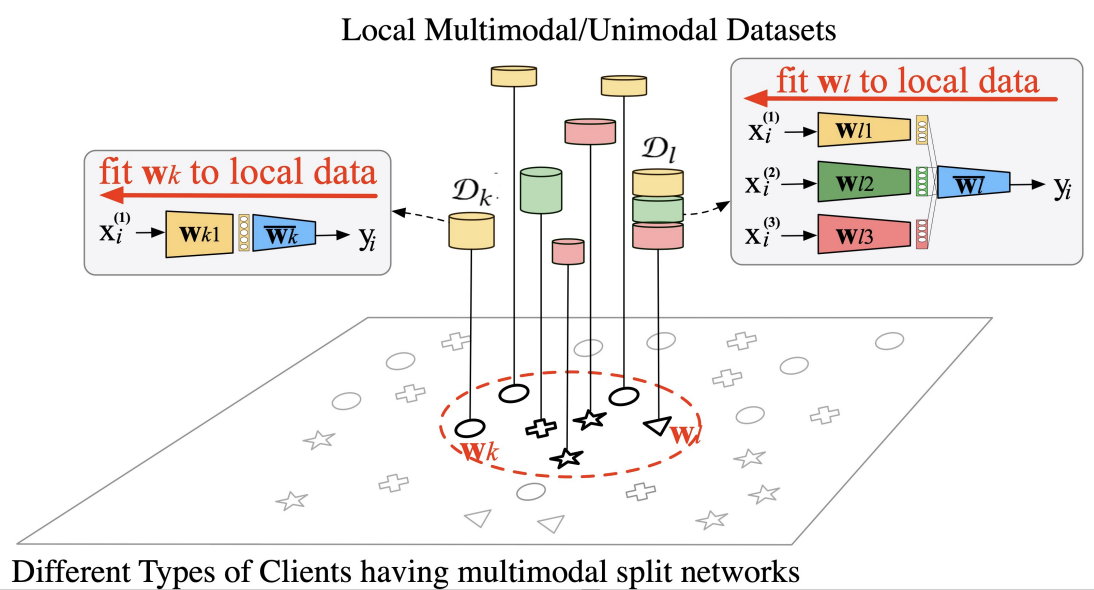
FedMSplit: Correlation-Adaptive Federated Multi-Task Learning across Multimodal Split Networks
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’22): Research Track, 2022
With the advancement of data collection techniques, end users are interested in how different types of data can collaborate to improve our life experiences. Multimodal Federated Learning (MFL) is an emerging area allowing many distributed clients, each of which can collect data from multiple types of sensors, to participate in the training of some multimodal data-related models without sharing their data. In this paper, we address a novel challenging issue in MFL, the modality incongruity, where clients may have heterogeneous setups of sensors and their local data consists of different combinations of modalities. With the modality incongruity, clients may solve different tasks on different parameter spaces, which escalates the difficulties in dealing with the statistical heterogeneity problem of federated learning; also, it would be hard to perform accurate model aggregation across different types of clients. To tackle these challenges, in this work, we propose the FedMSplit framework, which allows federated training over multimodal distributed data without assuming similar active sensors in all clients. The key idea is to employ a dynamic and multi-view graph structure to adaptively capture the correlations amongst multimodal client models. More specifically, we split client models into smaller shareable blocks and allow each type of blocks to provide a specific view on client relationships. With the graph representation, the underlying correlations between clients can be captured as the edge features in the multi-view graph, and then be utilized to promote local model relations through the neighborhood message passing in the graph. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method under different sensor setups with statistical heterogeneity.
-
×
![]()
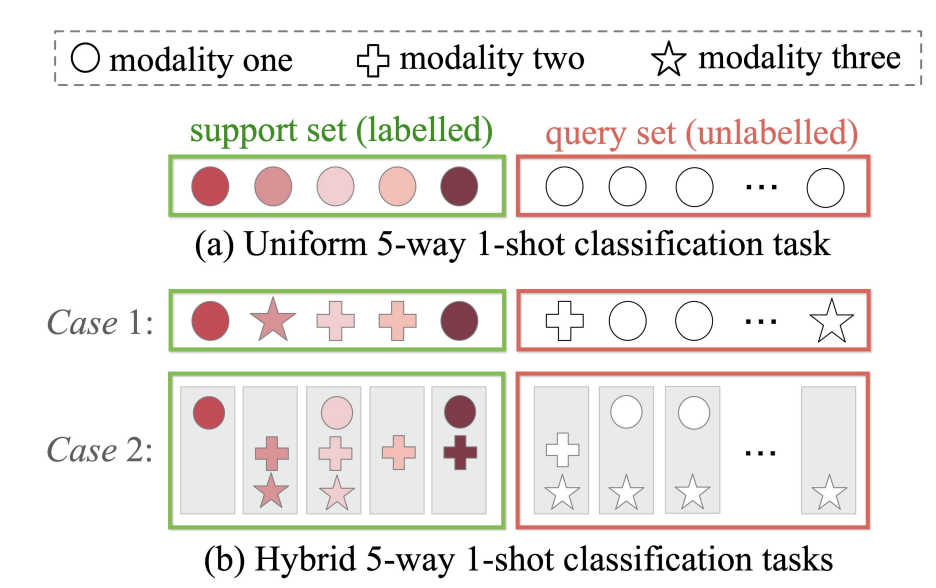
Topological Transduction for Hybrid Few-Shot Learning
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022 (WWW’22): Research Track
Digging informative knowledge and analyzing contents from the internet is a challenging task as web data may contain new concepts that are lack of sufficient labeled data as well as could be multimodal. Few-shot learning (FSL) has attracted significant research attention for dealing with scarcely labeled concepts. However, existing FSL algorithms have assumed a uniform task setting such that all samples in a few-shot task share a common feature space. Yet in the real web applications, it is usually the case that a task may involve multiple input feature spaces due to the heterogeneity of source data, that is, the few labeled samples in a task may be further divided and belong to different feature spaces, namely hybrid few-shot learning (hFSL). The hFSL setting results in a hybrid number of shots per class in each space and aggravates the data scarcity challenge as the number of training samples per class in each space is reduced. To alleviate these challenges, we propose the Task-adaptive Topological Transduction Network, namely TopoNet, which trains a heterogeneous graph-based transductive meta-learner that can combine information from both labeled and unlabeled data to enrich the knowledge about the task-specific data distribution and multi-space relationships. Specifically, we model the underlying data relationships of the few-shot task in a node-heterogeneous multi-relation graph, and then the meta-learner adapts to each task’s multi-space relationships as well as its inter- and intra-class data relationships, through an edge-enhanced heterogeneous graph neural network. Our experiments compared with existing approaches demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
-
×
![]()
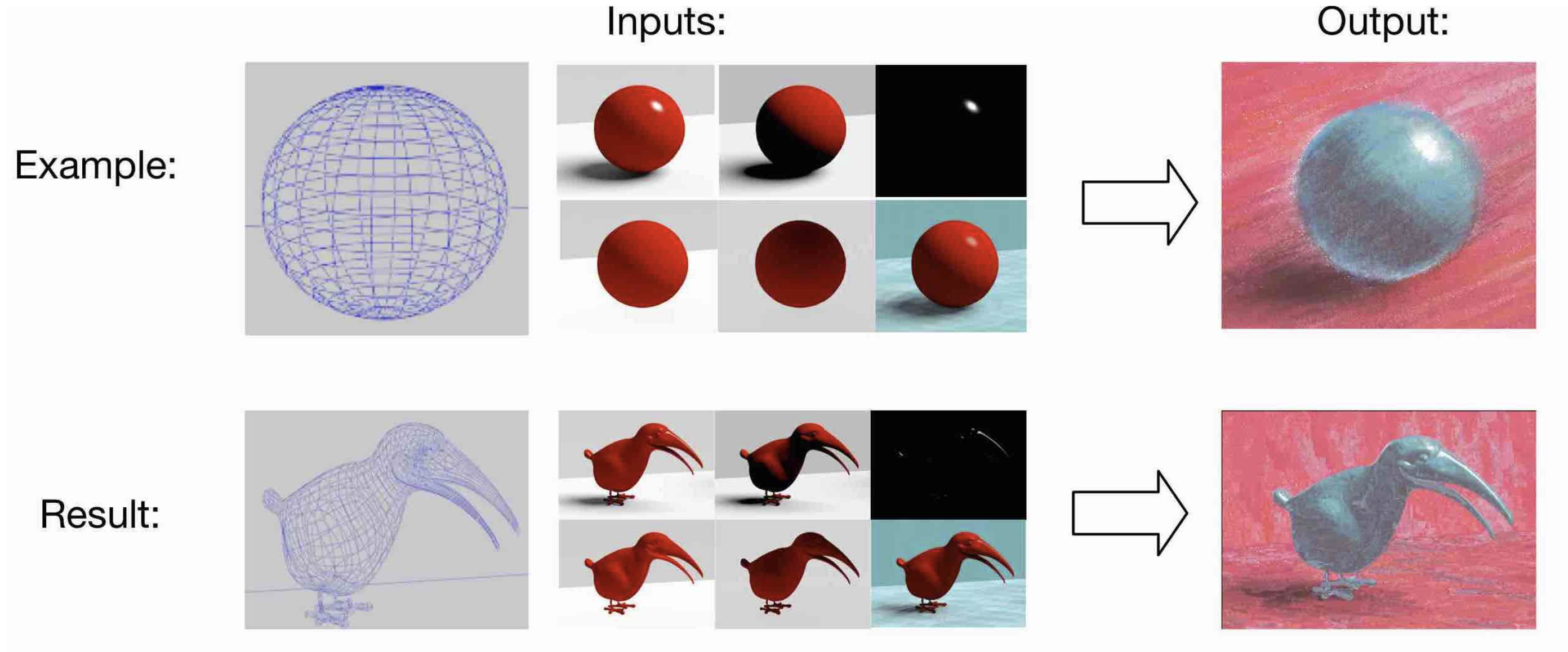
Deep Semantic Space guided Multi-scale Neural Style Transfer
Jiachen Yu, Li Jin, Jiayi Chen, Youzi Xiao, Zhiqiang Tian, and Xuguang Lan
In Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022
This work derived from my master’s thesis. Related repositories: https://github.com/jia-yi-chen/Painting3dModel
2021
-
×
![]()
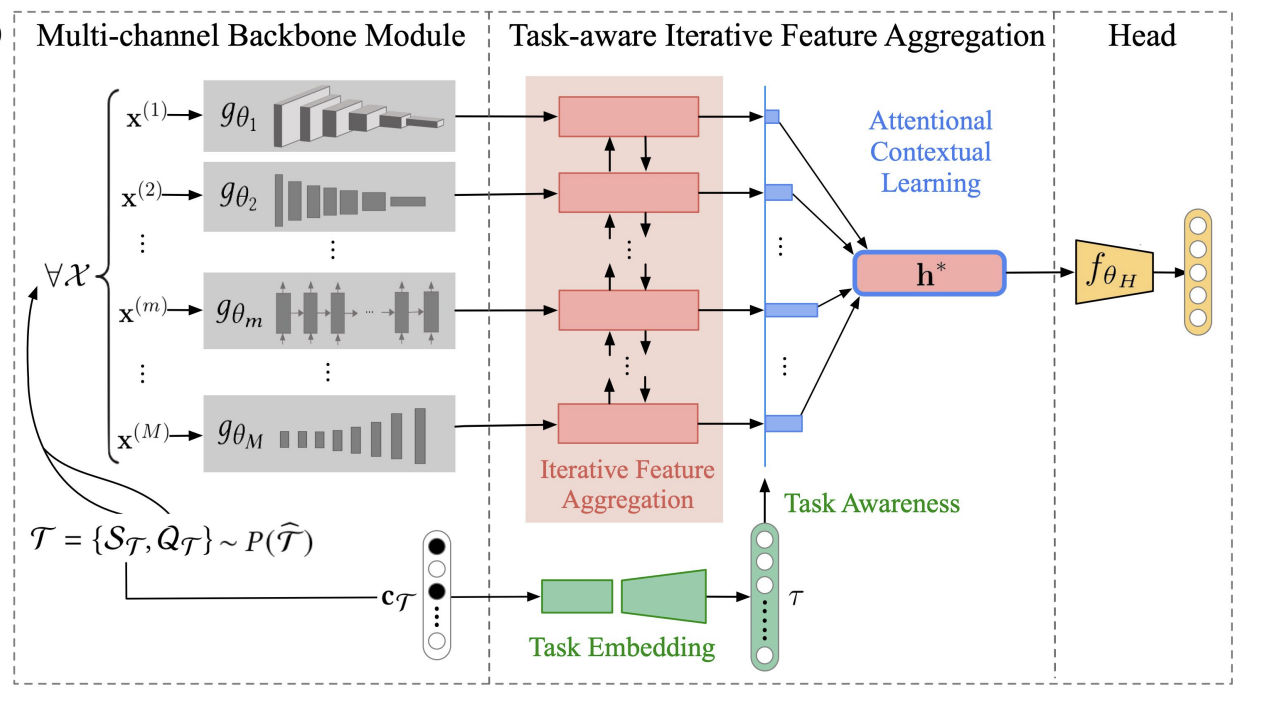
HetMAML: Task-Heterogeneous Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Few-Shot Learning Across Modalities
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management (CIKM’21): Full Paper, 2021
Most of existing gradient-based meta-learning approaches to few-shot learning assume that all tasks have the same input feature space. However, in the real world scenarios, there are many cases that the input structures of tasks can be different, that is, different tasks may vary in the number of input modalities or data types. Existing meta-learners cannot handle the heterogeneous task distribution (HTD) as there is not only global meta-knowledge shared across tasks but also type-specific knowledge that distinguishes each type of tasks. To deal with task heterogeneity and promote fast within-task adaptions for each type of tasks, in this paper, we propose HetMAML, a task-heterogeneous model-agnostic meta-learning framework, which can capture both the type-specific and globally shared knowledge and can achieve the balance between knowledge customization and generalization. Specifically, we design a multi-channel backbone module that encodes the input of each type of tasks into the same length sequence of modality-specific embeddings. Then, we propose a task-aware iterative feature aggregation network which can automatically take into account the context of task-specific input structures and adaptively project the heterogeneous input spaces to the same lower-dimensional embedding space of concepts. Our experiments on six task-heterogeneous datasets demonstrate that HetMAML successfully leverages type-specific and globally shared meta-parameters for heterogeneous tasks and achieves fast within-task adaptions for each type of tasks.
2020
-
×
![]()
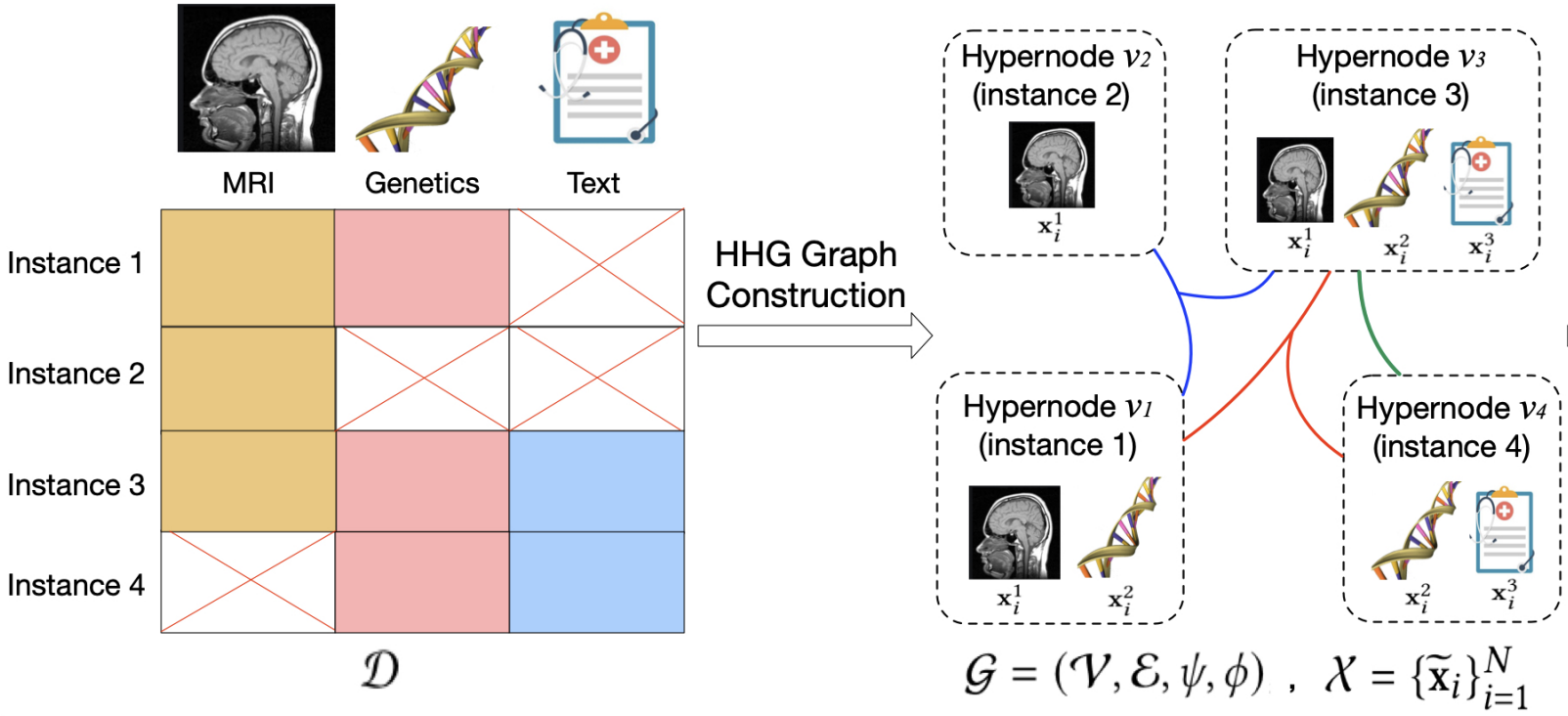
HGMF: Heterogeneous Graph-Based Fusion for Multimodal Data with Incompleteness
Jiayi Chen, and Aidong Zhang
In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining (KDD’20): Research Track, 2020
With the advances in data collection techniques, large amounts of multimodal data collected from multiple sources are becoming available. Such multimodal data can provide complementary information that can reveal fundamental characteristics of real-world subjects. Thus, multimodal machine learning has become an active research area. Extensive works have been developed to exploit multimodal interactions and integrate multi-source information. However, multimodal data in the real world usually comes with missing modalities due to various reasons, such as sensor damage, data corruption, and human mistakes in recording. Effectively integrating and analyzing multimodal data with incompleteness remains a challenging problem. We propose a Heterogeneous Graph-based Multimodal Fusion (HGMF) approach to enable multimodal fusion of incomplete data within a heterogeneous graph structure. The proposed approach develops a unique strategy for learning on incomplete multimodal data without data deletion or data imputation. More specifically, we construct a heterogeneous hypernode graph to model the multimodal data having different combinations of missing modalities, and then we formulate a graph neural network based transductive learning framework to project the heterogeneous incomplete data onto a unified embedding space, and multi-modalities are fused along the way. The learning framework captures modality interactions from available data, and leverages the relationships between different incompleteness patterns. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing graph-based as well as non-graph based baselines on three different datasets.
2019
-

×
![]()
Multi-scale Neural Style Transfer Based on Deep Semantic Matching
Jiachen Yu, Li Jin, Jiayi Chen, Zhiqiang Tian, and Xuguang Lan
In Cognitive Systems and Signal Processing, 2019
Existing Neural Style Transfer (NST) algorithms do not migrate styles well to a reasonable location where the output image can render the correct spatial structure of the object being painted. We propose a deep semantic matching-based multi-scale (DSM-MS) neural style transfer method, which can achieve the reasonable transfer of styles guided by the prior spatial segmentation and illumination information of input images. First, according to real drawing process, before an artist decides how to paint a stroke, he/she needs to observe and then understand subjects, segmenting space into different regions, objects and structures and analyzing the illumination conditions on each object. To simulate the two visual cognition processes, we define a deep semantic space (DSS) and propose a method for calculating DSSs using manual image segmentation, automatic illumination estimation and convolutional neural network (CNN). Second, we define a loss function, named deep semantic loss, which uses DSS to guide reasonable style transfer. Third, we propose a multi-scale optimization strategy for improving the efficiency of our method. Finally, we achieve an interdisciplinary application of our method for the first time–painterly rendering 3D scenes by neural style transfer. The experimental results show that our method can synthesize images in better original structures, with more reasonable placement of each styles and visual aesthetic feeling.
*This work derived from my master’s thesis. Related repositories: https://github.com/jia-yi-chen/Painting3dModel. A small 3D-to-2D dataset created using Corel Painter and Maya3D: https://github.com/jia-yi-chen/3dModel-to-2dArt-Dataset
-

×
![]()
Image Artistic Style Transfer Based on Color Distribution Preprocessing
Yinshu Zhang, Jiayi Chen, Xiangyu Si, Zhiqiang Tian, and Xuguang Lan
In Cognitive Systems and Signal Processing, 2019
Work derived from my master’s thesis. Related repositories: https://github.com/jia-yi-chen/Painting3dModel. Style transfer is an increasingly popular field that can capture the styles of a particular artwork and use them to synthesize a new image with specific content. Previous NST algorithms have the limitation to transfer styles to correct regions in the output image. Therefore, some regions in the output image have deformed structures of the source image. In this paper, we propose a color preprocessing-based neural style transfer method to overcome the limitation. To reduce impacts caused by color differences between source image and style, we propose three models based on a color iterative distribution transform algorithm (IDT). The first one is named original color-preprocessed (OCp) model, which uses IDT to transform the color probability density function (PDF) of source image into that of style image. The second one is named exposure-corrected original color-preprocessed (EC-OCp) model, which adds an automatic detail-enhanced exposure correction module before OCp model. When source image is underexposed, EC-OCp model can achieve better results than OCp model. The third one is style color-preprocessed (SCp) model. It uses IDT to transform the color PDF of style image into that of source image. The original structures are well protected in the output image. According to experiments, the proposed models are robust to the source images with more conditions. Therefore, they have more usage values than the original method.
2016
-
Efficient detail-enhanced exposure correction based on auto-fusion for LDR image
Jiayi Chen, Xuguang Lan, and Meng Yang
In 2016 IEEE 18th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP)
We consider the problem of how to simultaneously and well correct the over- and under-exposure regions in a single low dynamic range (LDR) image. Recent methods typically focus on global visual quality but cannot well-correct much potential details in extremely wrong exposure areas, and some are also time consuming. In this paper, we propose a fast and detail-enhanced correction method based on automatic fusion which combines a pair of complementarily corrected images, i.e. backlight & highlight correction images (BCI &HCI). A BCI with higher visual quality in details is quickly produced based on a proposed faster multi-scale retinex algorithm; meanwhile, a HCI is generated through contrast enhancement method. Then, an automatic fusion algorithm is proposed to create a color-protected exposure mask for fusing BCI and HCI when avoiding potential artifacts on the boundary. The experiment results show that the proposed method can fast correct over/under-exposed regions with higher detail quality than existing methods.